This next step is relatively simple it only consists of two steps so well show them all here C 3 H 3 O 3 pyruvate CH 3 COH acetaldehyde CO 2 CH 3 COH acetaldehyde NADH. As soon as the malt sugar has fermented the yeast sinks and is collected.
Secondary fermentation is not the best term to use there isnt another fermentation happing its the same one.
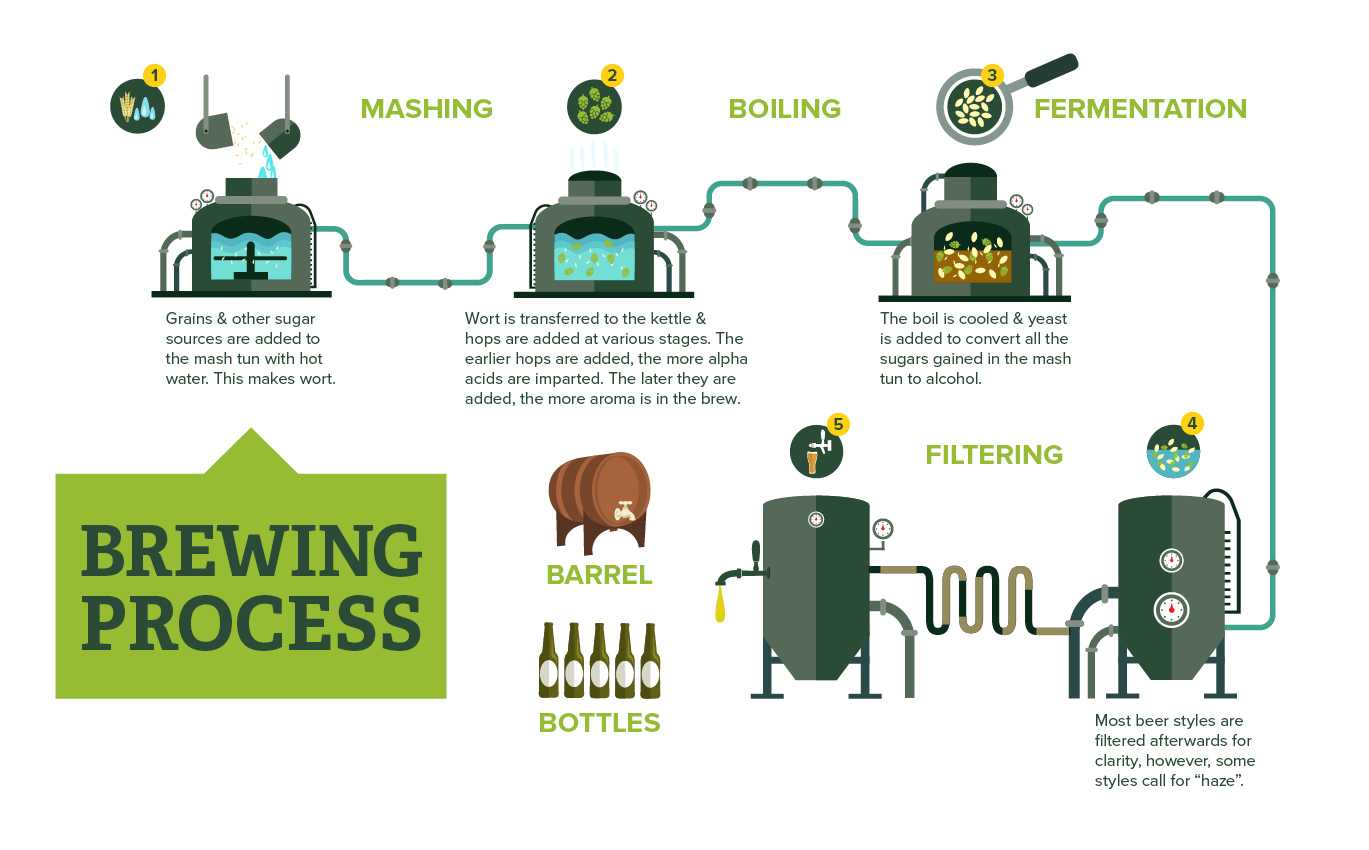
Fermentation of beer steps. For beer fermentation to occur you need yeast. As described in the in-depth post on yeast fermentation processes yeast converts glucose into carbon dioxide and ethanol during fermentation. This fermentation doesnt require any oxygen.
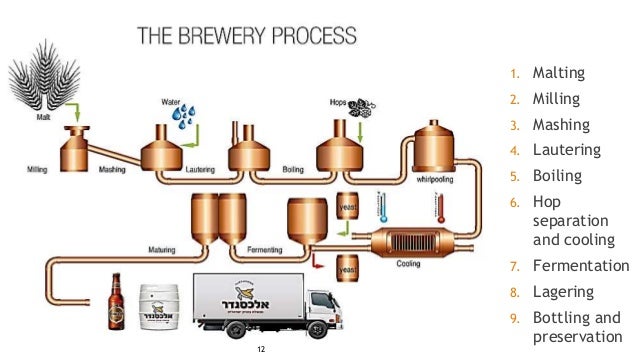
Yeasts are living micro organisms and need to be nurtured properly for them to thrive. Fermentation is the process by which yeast converts the glucose in the wort to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide gas – giving the beer both its alcohol content and its carbonation. To begin the fermentation process the cooled wort is transferred into a fermentation vessel to which the yeast has already been added.
Start by chilling the wort to the target fermentation temperature. Attach insulated temp robe to the side of the fermentor and pitch the yeast starter. This will take around 2-5 days.
After the 2-5 days of active fermentation remove the robe from the side of the fermenter. The fermentation process starts with the preparation of a liquid called mash or wort for brewing and distilling and must for the winemaking process. Regardless of the names these liquids are basically sugar water with some aromas of course.
To start the fermentation process beer yeast is added while the fermentation vessel is feeling filled. During fermentation yeast converts the sugary wort into actual beer by producing alcohol a wide range of flavours and carbon dioxide which is used later in the brewing process to carbonate the beer. The seventh step in the beer making process is the alcoholic fermentation.
This takes place in a fermentation tank where special brewing yeast is added. The yeast turns the malt sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide. As soon as the malt sugar has fermented the yeast sinks and is collected.
This young beer is not drinkable as it contains bad tasting and smelly compounds that are a result of the fermentation process. Two compounds that occur in high concentrations are butane-23-dione and pentane-23-dione both contain two ketone functional groups hence the name dione and they have very buttery tastes which is highly. Secondary fermentation is not the best term to use there isnt another fermentation happing its the same one.
Putting beer into a secondary fermenter just allows your beer to be pulled of the yeast cake it is the belief that yeast autolysis the death of the yeast cell is very common and you want to get your beer off the yeast cake by transferring the beer to another. Fermentation where it mixes with the incoming wort. Normally more yeast is produced during fermentation than is required by the brewery.
The surplus yeast is washed to recover as much beer as possible this wash-water is used for dilution later in the beer-making process and the yeast may then be sold. Step 5 - Maturation Vessel. If the yeast is fermenting the pyruvate will go into the fermentation process.
This next step is relatively simple it only consists of two steps so well show them all here C 3 H 3 O 3 pyruvate CH 3 COH acetaldehyde CO 2 CH 3 COH acetaldehyde NADH.